上一篇介紹Decorator實作,討論如何追蹤程式執行流程,並計算執行時間,找出作業的瓶頸。今天我們進一步討論Decorator更多的用法與應用實務,包括:
不管是Flask、Streamlit及其他套件使用的Decorator多帶有參數,要如何實現呢? 很簡單,只要在inner function加上參數處理即可。
範例1. 利用Decorator重複執行函數N次,使用【*args, **kwargs】,可接收任意個固定位置的參數(Positional arguments)及命名參數(Keyword arguments),可通用於所有函數。
def repeat(times):
def decorator(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
for _ in range(times):
func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return decorator
@repeat(3) # 3 會對應 times
def greet(name): # name 會對應 *args
print(f"Hello {name}!")
greet("Michael")
執行結果:
Hello Michael!
Hello Michael!
Hello Michael!
若要使用命名參數(Keyword arguments),可改為:
@repeat(3) # 3 會對應 times
def greet(name='x'): # name 會對應 *args
print(f"Hello {name}!")
greet(name="Michael")
執行結果與上述相同。
若被Decorator呼叫的函數帶有傳回值,則wrapper呼叫函數需return傳回值。
範例2. 利用Decorator重複執行函數N次,使用【*args, **kwargs】,可接收任意個固定位置的參數(Positional arguments)及命名參數(Keyword arguments),可通用於所有函數。
def log_decorator(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("呼叫函數前")
output = func(*args, **kwargs)
print("呼叫函數後")
return output
return wrapper
@log_decorator
def add(a, b):
return a + b
# 呼叫 add
print(add(1, 2))
執行結果:注意函數輸出,會在最後一行,因為Decorator執行並未列印輸出,而是在主程式最後才列印輸出值。
呼叫函數前
呼叫函數後
3
範例3. 也可以使用類別實作Decorator,下列程式會記錄Decorator被呼叫的次數,檔案名稱為decorator_class.py,程式修改自【Mastering Python Decorators: A Deeper Dive】。
# 宣告Decorator類別
class Counter:
def __init__(self, func): # 初始化
self.func = func
self.count = 0 # 記錄Decorator被呼叫的次數
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): # 物件建立後會自動執行此函數
self.count += 1 # 被呼叫的次數 + 1
print(f"被呼叫的次數:{self.count}")
return self.func(*args, **kwargs)
@Counter
def greet(name):
print(f"Hello {name}!")
# 測試
greet("Alice")
greet("Michael")
執行結果:
被呼叫的次數:1
Hello Alice!
被呼叫的次數:2
Hello Michael!
使用類別實作Decorator的時機主要有2個:
通盤了解Decorator概念後,我們就可以進行實際應用了。
範例4. 以Flask為例,以Decorator處理權限控管,核心程式不必檢查使用者是否已經登入,程式名稱為flask_auth.py。
from flask import Flask, request, redirect, url_for, render_template, session
import functools, os
app = Flask(__name__)
# 設定 session 的金鑰
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = os.urandom(24)
# 合格的使用者及密碼
user_store = {'michael':'1234', 'john':'12345'}
# Decorator:檢查使用者是否已經登入,我們以session記錄登入的使用者帳號。
def login_required(func):
"""Make sure user is logged in before proceeding"""
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper_login_required(*args, **kwargs):
if session.get('user', None) is None: # 使用者未登入
return redirect(url_for("login", next=request.url))
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper_login_required
@app.route("/", methods=['GET'])
@login_required
def index(): # 首頁
return "Home Page"
@app.route("/hello", methods=['GET'])
@login_required
def say_hello(): # 登入後重導至本頁
return "Hello " + session.get('user')
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
error = None
if request.method == 'POST':
# 登入檢查
if (request.form['username'] not in user_store.keys() or
request.form['password'] != user_store[request.form['username']]):
error = '帳密錯誤.'
else: # 登入成功
session['user'] = request.form['username']
return redirect(url_for('say_hello')) # 重導至 say_hello 函數
return render_template('login.html', error=error)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
<html>
<head>
<title>登入頁面</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@3.3.7/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-BVYiiSIFeK1dGmJRAkycuHAHRg32OmUcww7on3RYdg4Va+PmSTsz/K68vbdEjh4u" crossorigin="anonymous">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>登入(Login)</h1>
<br>
<form action="" method="post">
<input type="text" placeholder="帳號" name="username" value="{{
request.form.username }}">
<input type="password" placeholder="密碼" name="password" value="{{
request.form.password }}">
<input class="btn btn-default" type="submit" value="Login">
</form>
{% if error %}
<p class="error"><strong>Error:</strong> {{ error }}
{% endif %}
</div>
</body>
</html>
測試:執行python flask_auth.py,啟動server,再瀏覽http://localhost:5000/ 。
執行結果:重導至登入頁面,輸入帳密,例如michael/1234,成功的話,就會出現以下訊息。
Hello michael
登入頁面: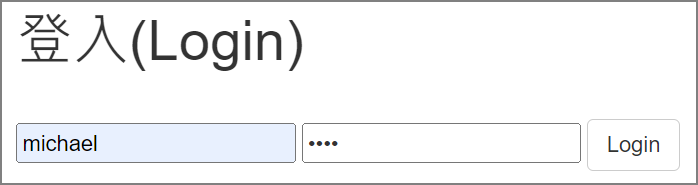
【12 Python Decorators to Take Your Code to the Next Level】列舉12種Decorator的簡單用途:
Decorator用途廣泛,可以將各式的關注點自核心程式抽離出去,讓我們專注在核心業務的開發,讓程式更模組化、更簡潔,是中大型系統開發必備的技能。
本系列的程式碼會統一放在GitHub,本篇的程式放在src/7資料夾,歡迎讀者下載測試,如有錯誤或疏漏,請不吝指正。
